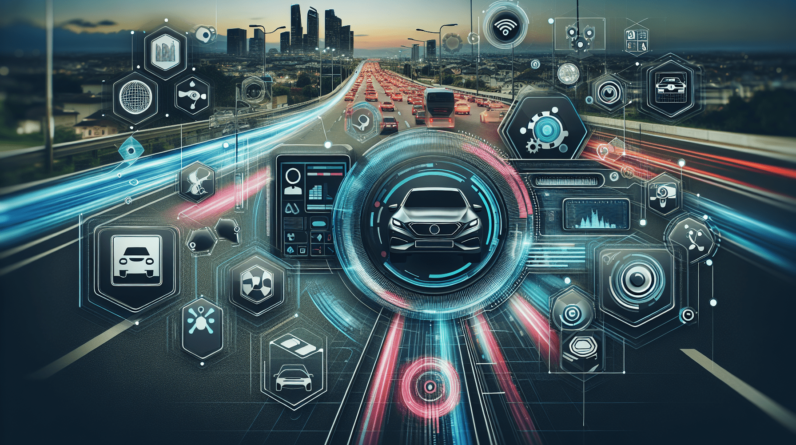
Have you ever wondered how your car senses potential hazards on the road, helps you stay in your lane, or even parks itself? The magic behind these features is called Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems, or ADAS. These systems have revolutionized the driving experience, making it safer, more efficient, and increasingly automated.
This image is property of images.spiceworks.com.
In need of auto care? Dial 913-605-3126 for remote or in-shop services!
What Are ADAS?
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems are a collection of electronic technologies that assist drivers in various functions to enhance safety and improve overall driving experience. These systems use sensors, cameras, radar, and other technologies to analyze data in real-time, providing you with support in areas like steering, braking, and monitoring your surroundings.
The Need for ADAS
The primary motivation behind ADAS is safety. Car accidents are a leading cause of fatalities worldwide, and human error is a major factor in most of these incidents. ADAS aims to reduce these errors by providing drivers with additional information and, in some cases, taking control of the vehicle to avoid collisions.
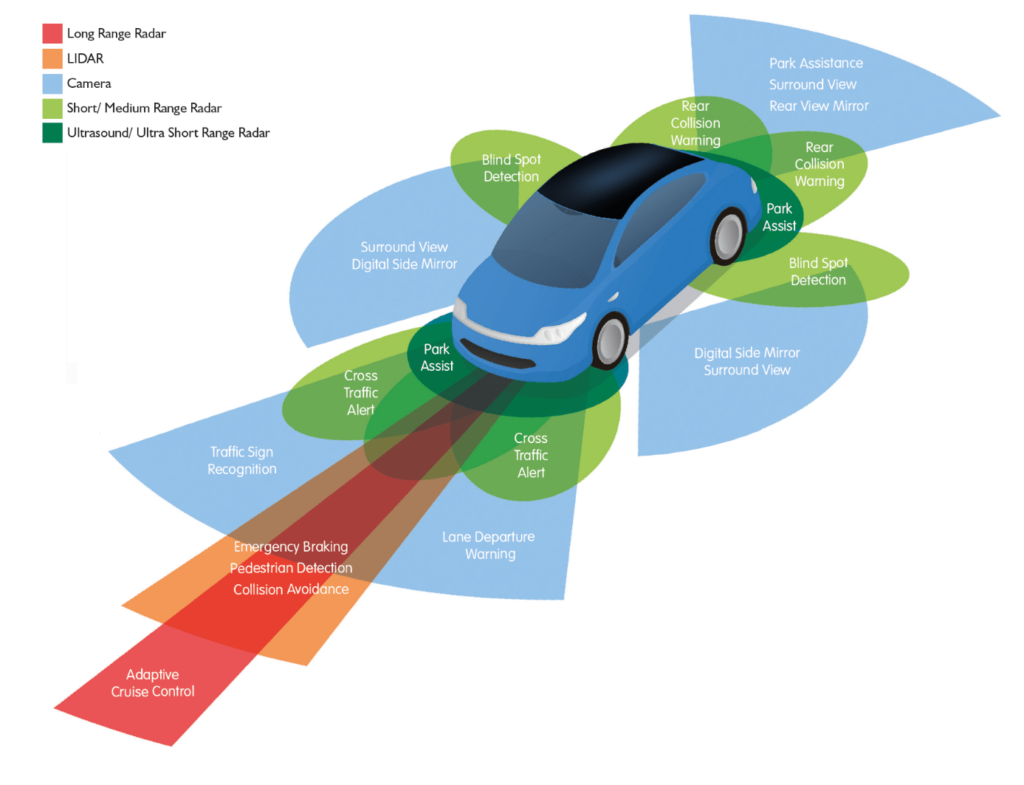
ADAS Components
To understand how ADAS works, it’s crucial to know its main components. Here are some of the key elements that make these systems function:
- Sensors: These include radar, lidar, ultrasonic sensors, and cameras that collect data about the vehicle’s surroundings.
- Processors: High-speed processors analyze data from the sensors for real-time decision-making.
- Actuators: These parts execute the commands, such as applying brakes, steering, or accelerating.
- Software Algorithms: Advanced algorithms process the data and trigger appropriate actions.
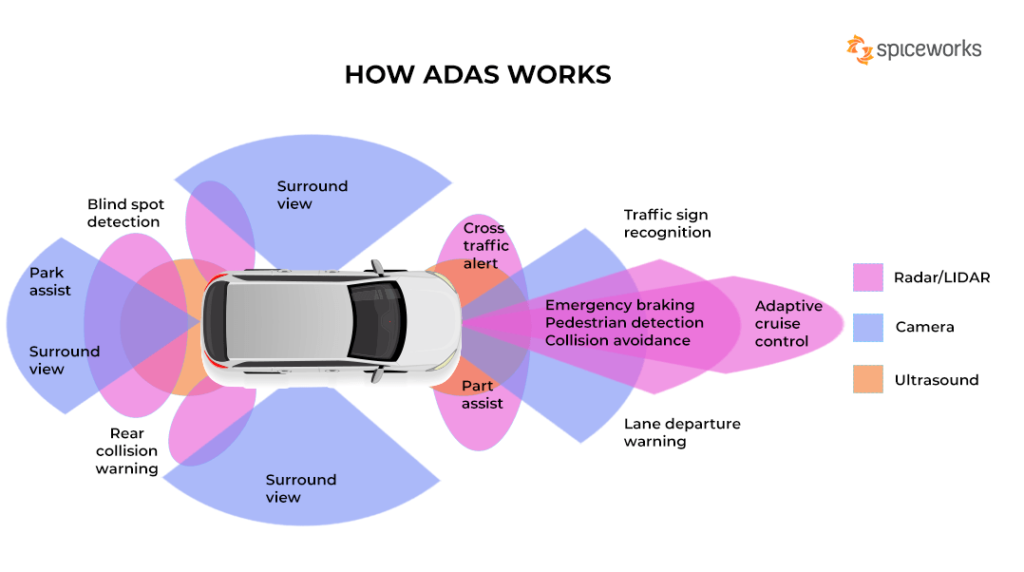
How ADAS Works
When you’re driving, ADAS continuously processes data from multiple sources to provide you with a safe and comfortable driving experience. Here is a simplified outline of how these systems generally function:
- Data Collection: Sensors collect real-time data about the environment, including the vehicle’s speed, surrounding objects, and road conditions.
- Data Processing: Advanced algorithms process this information to detect potential hazards.
- Decision Making: Based on the processed data, the system decides the necessary actions.
- Action Execution: Commands are sent to actuators to perform tasks like braking, steering, or alerting the driver.
Types of ADAS Features
ADAS can be broadly classified into various features that provide different kinds of assistance. Let’s discuss some of the most common ones you might encounter.
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
Imagine driving on the highway, keeping a steady speed without having to constantly adjust your distance from other vehicles. That’s ACC for you. It maintains a safe distance from the car ahead by automatically adjusting your speed. This can significantly reduce driver fatigue on long journeys.
Lane Keeping Assist (LKA)
Have you ever felt the car gently steer itself back into the lane when you drift out without signaling? That’s LKA at work. It uses cameras to detect lane markings and provides corrective steering or braking inputs to keep you within your lane.
Blind Spot Detection (BSD)
One of the most nerve-wracking aspects of driving is changing lanes. BSD makes this safer by using sensors and radars to monitor the areas you can’t see in your mirrors. It alerts you when there’s a vehicle in your blind spot, making lane changes safer.
Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB)
Ever been in a situation where you needed to brake suddenly? AEB can detect an imminent collision and apply the brakes automatically if you don’t react in time. This feature can greatly reduce the likelihood of accidents or at least lessen their severity.
Parking Assistance Systems
Do you dread parallel parking? Parking assistance systems can take that stress away. These systems use ultrasonic sensors to measure parking spaces and guide you into the spot by taking control of the steering while you manage the speed.
Traffic Sign Recognition (TSR)
Ever missed a speed limit sign or a stop sign? TSR reads road signs using cameras and displays the information on your dashboard, helping you stay informed and compliant with traffic laws.
Night Vision
Driving in the dark can be challenging. Night vision systems use infrared cameras to detect pedestrians, animals, and other obstacles that might not be visible with standard headlights. This feature often alerts you to hidden dangers and enhances your driving safety at night.
Driver Monitoring Systems
Fatigue and distraction are major causes of accidents. Driver monitoring systems use cameras to observe your behavior, like facial expressions and head movements, to detect signs of drowsiness or distraction. They can alert you, helping you stay alert and focused.
Head-Up Display (HUD)
HUD projects key information such as speed, navigation directions, and warning signals onto the windshield directly in your line of sight. This reduces the need for you to take your eyes off the road while checking essential data, making your driving safer.
This image is property of www.chipsaway.biz.
Advantages of ADAS
ADAS offers a wide range of benefits, making driving not just safer but also more comfortable and efficient.
Enhanced Safety
The main advantage is, without a doubt, enhanced safety. By assisting with critical functions like braking, lane-keeping, and collision detection, ADAS can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents caused by human error.
Reduced Driver Fatigue
Long drives can be exhausting. Features like adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assist can take some of the burdens off your shoulders, making long trips less tiring.
Improved Traffic Flow
ADAS can contribute to smoother traffic flow. For example, adaptive cruise control and automated braking help in maintaining a constant speed and safer distance between vehicles, reducing the chances of traffic jams.
Cost Savings
While some of these technologies might seem costly upfront, they can potentially save you money in the long run by reducing the likelihood of accidents and subsequent repair costs.
Insurance Benefits
Many insurers offer discounts if your vehicle is equipped with ADAS, recognizing the reduced risk of accidents. This can make a significant difference in your annual premiums.
Challenges and Limitations
While ADAS technologies are incredibly advanced, they are not without their challenges and limitations.
Sensor Limitations
Sensors can sometimes fail to detect objects under certain conditions, such as heavy rain, fog, or snow. This can lead to potential system failures or false alerts.
High Costs
The initial cost of these systems can be high, making them less accessible for budget-conscious consumers. Over time, as the technology becomes more widespread, prices are expected to drop.
Driver Over-Reliance
There’s a risk that drivers might become too reliant on these systems, paying less attention to their surroundings. It’s crucial to remember that ADAS is there to assist, not replace, human intervention.
Compatibility Issues
Not all ADAS features are compatible with every vehicle type. Make sure to consult your vehicle manufacturer to understand the limitations and capabilities of the system in your car.
Ethical and Legal Issues
As we move closer to fully autonomous vehicles, questions about legal responsibility and ethical issues come into play. Who is liable in case of an accident? These are complex questions that regulators and manufacturers are still working to answer.

This image is property of www.aeswave.com.
ADAS and Autonomous Driving
ADAS is a crucial stepping stone towards fully autonomous driving. While fully self-driving cars are not yet widespread, the functionalities provided by ADAS are building that path. Autonomous vehicles will rely heavily on the technologies and data collection methods pioneered by ADAS.
Levels of Automation
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has defined six levels of driving automation, from level 0 (no automation) to level 5 (full automation). ADAS features generally fall within levels 1 to 3, where they assist with driving tasks but still require human oversight.
| Level | Description | Examples of ADAS Features |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No Automation | Basic driver alerts |
| 1 | Driver Assistance | Adaptive Cruise Control |
| 2 | Partial Automation | Lane Keeping Assist, ACC |
| 3 | Conditional Automation | Traffic Jam Assist, Highway Pilot |
| 4 | High Automation | Fully autonomous in certain conditions |
| 5 | Full Automation | Fully autonomous in all conditions |
Future of Autonomous Vehicles
As technologies evolve, future cars will likely see more integration and optimization of ADAS features. This will pave the way for higher levels of autonomy, reducing the need for human intervention and making driving even safer and more efficient.
Conclusion
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) offer a range of benefits from increased safety to enhanced comfort and efficiency in driving. These systems work cohesively to provide real-time support, making your driving experience not only easier but significantly safer. While there are challenges to overcome, particularly in terms of cost and sensor limitations, the ongoing advancements in technology promise to make ADAS even more reliable and accessible in the years to come.
In essence, ADAS represents a significant technological leap forward, shaping the future of how we interact with our vehicles and setting the foundation for fully autonomous driving. So next time you get behind the wheel, remember that you’re experiencing the forefront of automotive innovation.
Need auto care? Call 913 605-3126 for remote or in-shop services!










