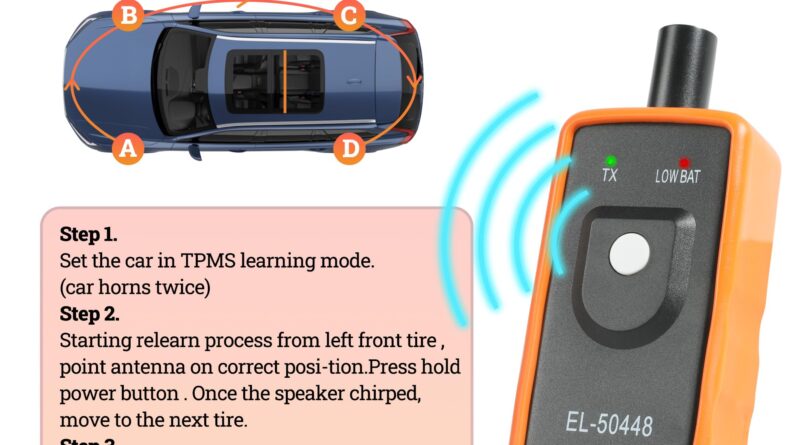
Have you ever wondered what that little horseshoe-shaped warning light on your dashboard means? If so, you’re not alone. Many drivers are curious about the Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) in their vehicles but aren’t sure exactly how it works or why it’s important. This guide will take you on a friendly journey to understand the ins and outs of TPMS, arming you with the knowledge to be a more informed and confident driver.

This image is property of www.bonabros.com.
Need auto care? Call 913 605-3126 for remote or in-shop services!
What is TPMS?
TPMS stands for Tire Pressure Monitoring System. It’s an electronic system that monitors the air pressure inside your vehicle’s tires. If the pressure drops below a certain threshold, a warning light illuminates on your dashboard. This system is crucial for your safety, fuel efficiency, and tire lifespan.
Responsibilities of TPMS
The TPMS has multiple roles in ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly. These responsibilities include:
- Alerting Low Tire Pressure: The primary function is to alert you when one or more tires are underinflated, which can lead to unsafe driving conditions.
- Improving Fuel Efficiency: Proper tire pressure helps in maintaining optimal fuel efficiency. Under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance, which means your engine has to work harder.
- Extending Tire Life: Correct tire pressure minimizes tire wear, enhancing their lifespan and saving you money in the long run.
- Ensuring Safety: Maintaining the proper tire pressure reduces the risk of tire failures, such as blowouts, which can lead to severe accidents.
Types of TPMS
There are two main types of Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems: Direct TPMS and Indirect TPMS. Both systems aim to ensure that your tires are always inflated properly but do so in different ways.
Direct TPMS
Direct TPMS uses pressure sensors inside each tire to directly measure the air pressure. These sensors send real-time information to your vehicle’s onboard computer.
Advantages of Direct TPMS
- Accuracy: Provides precise tire pressure readings.
- Immediate Alerts: Instant notification of any changes in tire pressure.
- Tire-Specific Information: Can pinpoint which tire is under-inflated.
Disadvantages of Direct TPMS
- Cost: Generally more expensive to install and maintain.
- Battery Life: Sensors run on batteries that may need replacement.
Indirect TPMS
Indirect TPMS does not measure tire pressure directly. Instead, it uses the vehicle’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) to monitor wheel rotation speeds. If a tire is under-inflated, it will rotate at a different speed compared to properly inflated tires.
Advantages of Indirect TPMS
- Cost-Effective: Usually cheaper to install and maintain.
- Less Maintenance: No batteries in sensors to replace.
Disadvantages of Indirect TPMS
- Less Accurate: Can be less precise in measuring actual tire pressure.
- Delayed Alerts: May take longer to notify you of a tire pressure issue.

This image is property of assets.bridgestonetire.com.
How Does TPMS Work?
Understanding how TPMS works can help you better appreciate its importance and functionalities. Each type of TPMS—Direct and Indirect—has a different working mechanism.
Direct TPMS Working Mechanism
- Pressure Sensors: Located inside each tire, these sensors measure the air pressure directly.
- Signal Transmission: The sensors transmit tire pressure data to the TPMS control module via wireless signals.
- Dashboard Alert: The control module analyzes the data, and if it detects a drop in tire pressure below a predetermined level, it illuminates the warning light on your dashboard.
Indirect TPMS Working Mechanism
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors are part of your vehicle’s ABS.
- Rotation Analysis: The TPMS control module uses the data from the ABS sensors to monitor wheel rotation speeds.
- Dashboard Alert: If a tire is under-inflated, its rotation speed changes, triggering the TPMS control module to illuminate the warning light on your dashboard.
Importance of Maintaining Proper Tire Pressure
Proper tire pressure is not just about avoiding that annoying dashboard light; it’s a critical aspect of vehicle safety and performance. Here’s why maintaining the correct tire pressure is so important:
Safety
Under-inflated tires can lead to dangerous driving conditions, such as:
- Poor Handling: Affects your ability to control the vehicle, especially in wet conditions.
- Increased Stopping Distance: Makes your vehicle take longer to come to a stop.
- Tire Blowouts: Higher risk of tire failures, which can cause accidents.
Fuel Efficiency
Driving on under-inflated tires can reduce your fuel efficiency by as much as 3-5%, meaning you will spend more money on gas over time.
Tire Longevity
Correct tire pressure ensures even tire wear, extending the life of your tires and saving you money in the long run.
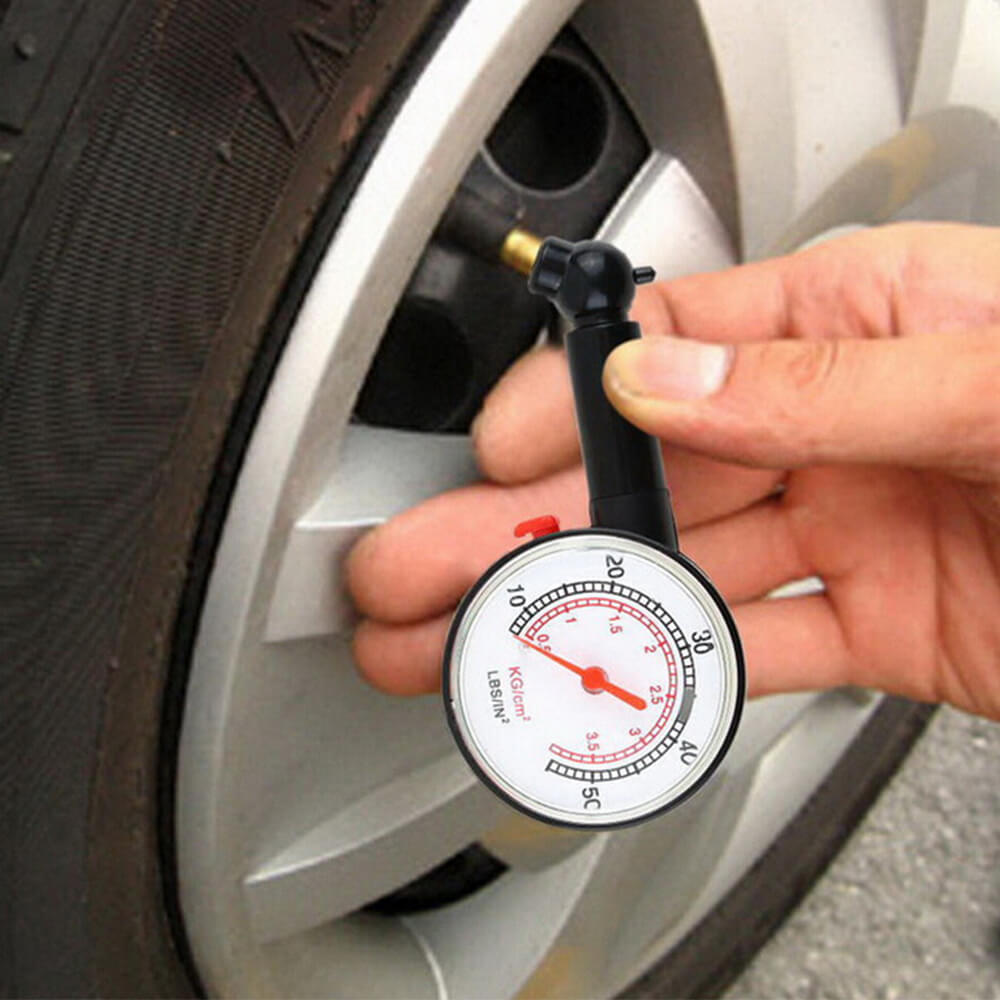

This image is property of www.bonabros.com.
Common Reasons for Tire Pressure Loss
Knowing why tire pressure changes can help you maintain optimal levels. Here are some common reasons why your tire pressure might decrease:
Temperature Changes
Tire pressure can drop by about 1 psi for every 10-degree drop in temperature. This means you may need to make adjustments as the seasons change.
Punctures and Leaks
Sharp objects like nails and screws can puncture your tires, leading to slow leaks.
Natural Permeation
Over time, air naturally escapes from tires even if there are no punctures, usually at a rate of 1-2 psi per month.
Valve Stem Issues
Faulty valve stems or valve cores can result in slow leaks, affecting your tire pressure over time.
Poor Rim Seal
Sometimes the seal between the tire and the rim can be imperfect, leading to gradual tire pressure loss.
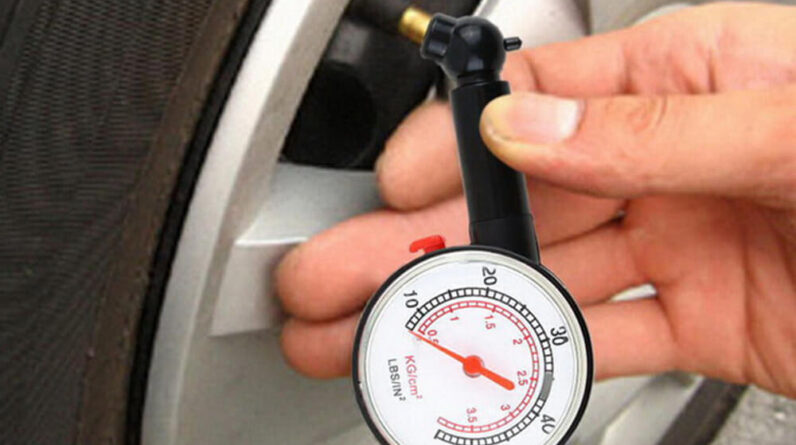
How to Check Tire Pressure
You should check your tire pressure regularly to ensure it remains at optimal levels. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you out:
Tools You’ll Need
- Tire Pressure Gauge
- Air Compressor (available at gas stations)
Steps to Check Tire Pressure
- Find the Recommended Pressure: Look for the recommended tire pressure in your vehicle’s owner manual or the tire placard located on the driver’s side door jamb.
- Remove the Valve Cap: Take off the valve cap from the tire you’re checking.
- Attach the Gauge: Press the tire pressure gauge onto the valve stem and take the reading.
- Compare and Adjust: Compare the gauge reading to the recommended pressure. If it’s low, add air using an air compressor. If it’s high, release some air.
- Recheck: Double-check the pressure to ensure it’s correct.
- Replace the Valve Cap: Put the valve cap back on once you’ve finished.
Frequency of Checks
It’s a good practice to check your tire pressure at least once a month and before long trips.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
What To Do If Your TPMS Light Comes On
Seeing the TPMS light can be concerning, but don’t panic. Here are the steps you should take if your TPMS light illuminates:
Immediate Steps
- Check Tire Pressure: As soon as it’s safe, check the pressure in all your tires, including the spare if your vehicle has one.
- Add Air if Needed: If any tire is under-inflated, add air to reach the recommended pressure.
- Monitor the Light: If the light turns off after adjusting the pressure, you’re good to go.
Continuous TPMS Light
If the TPMS light stays on even after adjusting the tire pressure, consider the following:
- Inspect for Damage: Look for punctures or damage on each tire.
- Consult a Professional: There could be an issue with the TPMS sensors or system itself, requiring professional diagnosis.
Flashing TPMS Light
A flashing TPMS light usually indicates a problem with the TPMS itself rather than tire pressure. In this case, you should:
- Refer to the Manual: Check your vehicle’s owner manual for specific guidance.
- Visit a Mechanic: A professional can diagnose and fix issues within the TPMS system.
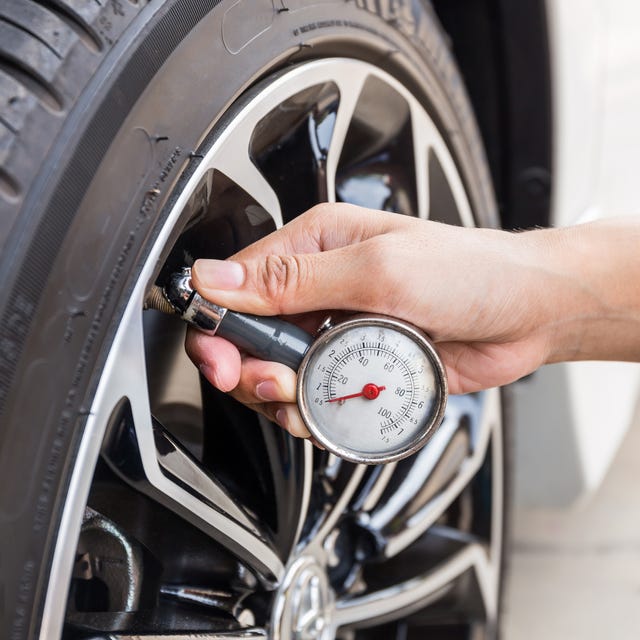
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance can help avoid TPMS issues and ensure your tires remain in top condition. Here are some preventive measures you can take:
Consistent Tire Pressure Checks
Make it a habit to check your tire pressure regularly, at least once a month and before long journeys.
Oversee Tire Rotations
Regular tire rotations help ensure even tire wear, which can prevent pressure imbalances and extend the life of your tires.
Balance Your Tires
Balanced tires contribute to a smoother ride and help maintain even tire pressure.
Inspect Tires for Damage
Regularly inspect your tires for signs of wear, punctures, or other damage that could lead to pressure loss.
Replace Worn-Out Tires
Old or worn tires are more susceptible to leaks and blowouts. Replace them according to your vehicle’s recommended intervals.

This image is property of hips.hearstapps.com.
FAQs About TPMS
You might still have some questions, and that’s totally okay. Here are some frequently asked questions about TPMS that might clear up any lingering doubts.
What Should I Do if My TPMS Sensor is Faulty?
If you suspect a faulty TPMS sensor, consult a professional mechanic to diagnose and replace the defective sensor.
Can I Drive My Car with the TPMS Light On?
While it’s possible to drive with the TPMS light on, it’s not advisable. Low tire pressure can be dangerous, impacting your vehicle’s handling and safety.
How Often Should TPMS Sensors Be Replaced?
TPMS sensors generally last 5-10 years. Check your vehicle’s owner manual for specific recommendations and get the sensors checked during routine maintenance.
Do I Need to Reset TPMS After Adding Air?
Most TPMS systems will automatically reset after the correct pressure is restored, but some vehicles may require manual resetting. Refer to your owner manual for instructions.
Is TPMS Mandatory in All Vehicles?
In many countries, including the United States, TPMS has been mandatory in all new passenger vehicles since 2008. Check your local regulations for specific requirements.
How Much Does It Cost to Replace a TPMS Sensor?
The cost to replace a TPMS sensor can vary widely, ranging from $50 to $100 per sensor, inclusive of labor, depending on your vehicle and where you get the service.
Final Thoughts
Understanding your vehicle’s Tire Pressure Monitoring System is essential for ensuring your safety, maintaining fuel efficiency, and extending the life of your tires. By knowing how TPMS works, the types of systems available, and how to respond to various TPMS alerts, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and avoid potential hazards on the road.
Taking proactive steps such as regular tire pressure checks, maintaining your tires through rotations and inspections, and addressing TPMS alerts promptly will help you get the most out of your TPMS. It’s a small investment of time that pays off in safety and savings.